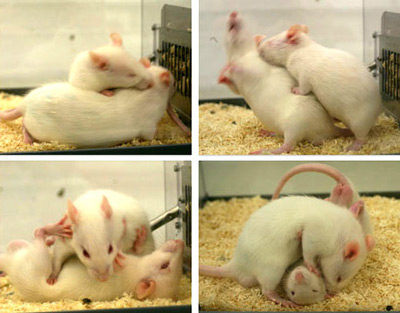
Rats exhibit fascinating behaviors that mirror social interactions seen in humans, making rat behavior and autism an intriguing area for research. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) now allow scientists to explore the subtle nuances of social behavior in rats, shedding light on the neural mechanisms that may relate to autism. By studying social behavior in rats, researchers aim to uncover the biological roots of autism and how these social creatures interact in complex ways. This innovative approach merges machine learning in behavioral research with the investigation of social dynamics, leading to greater insights into understanding autism. As we delve deeper into rat social interactions, the potential to enhance our comprehension of both rat behavior and human autism continues to grow.
The study of rodent social dynamics presents a compelling opportunity to advance our knowledge of neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism. By investigating the social interactions of these small mammals, researchers can uncover behavioral patterns and neural processes that might inform our understanding of human social behavior. Utilizing technology like machine learning and artificial intelligence in animal studies enriches the analysis of how social gestures and reactions are formed. This research not only seeks to clarify the complexities surrounding autism but also highlights the parallels between non-human animals and human conditions, opening doors for new therapeutic strategies. Expanding the framework from rats to broader behavioral contexts can significantly enhance our grasp of social engagement and its underlying genetic influences.
Understanding Rat Social Interactions
Rats are inherently social animals, exhibiting complex patterns of behavior that mirror human social interactions. Their communication involves not just vocalizations but intricate body language and physical touch, crucial for building social bonds within their groups. By observing these behaviors, researchers can gain insights into the underlying social structures that guide rat interactions, opening up new avenues for understanding social behavior in other species, including humans. This fascinating similarity suggests that we could leverage rat behavior to explore fundamental questions about how sociality evolves and functions in more complex organisms.
The new AI methods, equipped with advanced machine learning algorithms, have transformed the way these social interactions are studied. Instead of relying on subjective human interpretation, researchers can now quantify and analyze rat behavior with unprecedented accuracy. By tracking over 110 million 3D poses, scientists are mapping the nuances of rat social life. This technological advancement not only helps in understanding social behavior in rats but also lays the groundwork for comparative studies in social cognition across species.
The Intersection of AI and Animal Behavior Research
Artificial Intelligence has become a powerful tool in behavioral research, allowing for more rigorous analysis of animal interactions. Traditional methods often involved long hours of watching video footage, which limited the scope of data analysis. With AI’s ability to process large datasets swiftly, researchers can identify subtle behavioral patterns that might have gone unnoticed. This evolution in research methodology exemplifies how AI can bridge the gap between technology and biology, enhancing our understanding of animal behavior in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Incorporating machine learning into the study of rat behavior enables researchers to develop more sophisticated models of social interaction. The ability to observe and quantify behaviors with high precision can illuminate the underlying mechanisms driving animal behavior, from simple gestures to complex social dynamics. This AI-driven approach not only augments the current understanding of rat social lives but also paves the way for similar methodologies to be applied in broader contexts, including the study of human behavioral disorders such as autism.
Rat Behavior and Autism: Insights from Animal Models
The exploration of rat behavior provides a promising avenue for understanding autism, a condition that entails significant variations in social interactions and communication. Recent studies have shown that specific genetic modifications in rats can lead to behavioral changes that parallel aspects of autism spectrum disorders in humans. By analyzing these genetically altered rats, researchers can delve into the correlation between genetics and social behavior, thus gaining valuable insights into the biological underpinnings of autism.
These animal models allow scientists to investigate how mutations affect brain function and, consequently, social behavior. It becomes crucial to learn how particular genes influence social interactions in rats, which may reflect similar pathways in human autism. The ongoing research aims to identify specific brain circuits that contribute to differences in behavior, potentially leading to breakthroughs in therapeutic approaches. This intersection of rat behavior and autism research not only enhances our comprehension of social disorders but also highlights the importance of genetic factors in shaping social engagement.
Machine Learning in Behavioral Research: A Game Changer
The advent of machine learning in behavioral research has revolutionized the way scientists approach the study of animal interactions. This innovative technology allows researchers to automate the analysis of complex social behaviors, transforming large volumes of observational data into actionable insights. As a result, researchers can now examine behavioral patterns with unprecedented granularity, making it possible to identify and track interactions that may indicate deeper underlying mechanisms of behavior.
For instance, by applying machine learning techniques to rat behavior studies, researchers can analyze the impact of various social interactions on the learning processes of these animals. This comprehensive understanding of behavior not only sheds light on the social dynamics present within rat communities but also informs broader discussions about the evolution of social behavior across species. The insights gained through such studies contribute significantly to the field of animal behavior, showcasing how technology can enhance traditional methodologies.
The Role of Social Behavior in Rats
Social behavior in rats plays a crucial role in their survival and adaptation as species. These creatures thrive in social environments, where they establish hierarchies and engage in cooperative behaviors that ensure the welfare of the group. The nuanced ways in which rats interact—such as grooming and sharing resources—serve not only as a means of maintaining social bonds but also as an essential survival strategy in the wild. By studying the intricacies of these social dynamics, scientists can glean important lessons about the evolutionary success of social structures in animals.
Moreover, understanding rat social behavior provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of sociality in more complex organisms, including humans. The parallels drawn between rat interactions and human behaviors suggest that many fundamental aspects of social communication may have deep evolutionary roots. Researchers can explore how these mechanisms manifest in different species, thereby contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of social behavior as a whole. This knowledge can be especially beneficial in the context of developing interventions for social dysfunction in humans.
Exploring the Genetic Basis of Social Interaction
Investigating the genetic basis of social behavior in rats has become a focal point for understanding complex traits such as social interaction. By utilizing genetically modified rat models, researchers can discern how specific genes contribute to behavioral variations. This approach not only aids in identifying the biological factors underpinning social behavior but also enables scientists to draw parallels between animal models and human conditions, such as those seen in autism spectrum disorders.
This genetic exploration allows researchers to examine how variations in certain genes influence the development of social skills and interactions in rats. By analyzing the resulting behaviors, scientists can gain insights into how similar genetic factors may influence social behavior in humans. Ultimately, unraveling the genetic links to social interaction in rats could inspire new therapeutic interventions for social behavioral disorders, illustrating the importance of genetic research in the context of behavioral science.
Advancements in Tracking Animal Movement
The development of advanced tracking technologies has greatly enhanced the study of animal movement, particularly in understanding social behavior. By employing sophisticated imaging systems and AI algorithms, researchers are now able to monitor and analyze the movements of rats in real-time. This capability allows for a comprehensive assessment of how rats navigate their social environments, providing invaluable data for studying the intricacies of animal interactions.
These tracking advancements facilitate the exploration of behavioral patterns that were previously elusive. For instance, by visualizing how rats interact through gesture-based communication, researchers can gather insights that deepen our understanding of social interactions. The data generated from these advanced tracking systems not only contributes to the field of animal behavior but also informs our understanding of how such interactions might relate to human social behavior, particularly concerning disorders such as autism. Innovations in tracking technology thus serve as a powerful tool for bridging the knowledge gap between animal and human behavioral studies.
Implications of Rat Research for Human Health
The implications of rat behavior research extend far beyond the laboratory, offering potential insights into human health, particularly in understanding neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism. By examining the social behaviors of genetically modified rats, researchers can model the effects of altered genes on behavior, which can parallel similar effects observed in humans. This comparison provides critical information that could lead to breakthroughs in therapy and treatment options for conditions that affect social interactions.
Moreover, the shared biological and behavioral features between rats and humans make them ideal model organisms for studying complex disorders. Behavioral research utilizing rats can shed light on how environmental factors, combined with genetic predispositions, influence social development. By translating findings from rat studies to therapeutic strategies for humans, scientists can develop more effective interventions aimed at improving quality of life for those with social behavior disorders.
Data Sharing and Collaborative Research in Behavioral Science
The commitment to sharing data from rat behavior studies marks a significant step forward in collaborative research within the field of behavioral science. By making their data publicly available, researchers promote transparency and encourage others in the scientific community to engage with their findings. This collaborative approach amplifies the potential for developing better models of how the brain influences social behavior and fosters a collective effort to advance the understanding of complex behavioral phenomena.
Furthermore, pooling resources and data creates opportunities for researchers to validate findings and explore new hypotheses. With many researchers analyzing the same datasets, the potential for discovering new insights into social behavior increases substantially. This culture of collaboration not only enhances the research landscape but also accelerates the development of innovative therapies and interventions for social behavior disorders in both animals and humans.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can studying social behavior in rats help us understand autism?
Studying social behavior in rats provides insights into the brain-behavior link, particularly in how social interactions mirror those seen in humans with autism. Research utilizing machine learning to analyze rat social behaviors can reveal variations in social interactions that parallel human behaviors associated with autism spectrum disorders.
What role does AI play in researching rat behavior and autism?
AI enhances research on rat behavior by enabling the analysis of large datasets from rat interactions, helping to identify patterns and variations in social behavior. This method can facilitate a better understanding of the neurological aspects of autism, as data from genetically modified rats can inform how specific genes influence social behaviors.
What observations about rat social interactions can inform our understanding of autism?
Observations of rat social interactions, such as how they communicate through body language, can help identify behavioral parallels to autism. Just as children on the autism spectrum may display unique social behaviors, genetically modified rats exhibit varying social interaction styles, shedding light on the genetic underpinnings of social behavior.
How does machine learning contribute to the study of rat behavior related to autism?
Machine learning contributes by providing a robust framework for quantifying rat behavior with high precision. By analyzing over 110 million 3D poses of rat movements and interactions, researchers can uncover intricate details about social behaviors that may be linked to autism-related genetic variations.
What are the implications of using rats to understand the spectrum of autism?
Using rats to understand autism’s spectrum offers a unique opportunity to explore the biological basis of social behavior. Variability in rat social interactions associated with different genes can help researchers identify the mechanisms through which genetic mutations influence social behavior, potentially informing therapeutic approaches for autism.
Why are rats considered a valuable model for studying autism?
Rats are a valuable model for studying autism due to their complex social behaviors that can be quantitatively analyzed. The ability to manipulate genetic factors in rat models allows researchers to draw parallels between rat and human social behavior, enhancing our understanding of autism’s varying presentations across individuals.
What future research directions could stem from studying rat social behavior in autism research?
Future research could focus on pinpointing neural circuits responsible for differences in social behavior observed in both rats and humans. This could lead to innovative therapeutic strategies aimed at addressing social deficits present in autism spectrum disorders.
How can understanding rat social interactions impact therapies for autism?
Understanding rat social interactions can inform therapies for autism by uncovering genetic and neurological correlates of social behavior. Insights gained may inspire new therapeutic approaches tailored to improve interpersonal skills and social engagement in individuals with autism.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Methodology | New AI techniques track rat social interactions to understand behavior. |
| Social Behavior | Rats show complex social patterns similar to human interactions. |
| Research Implications | Findings may offer insights into disorders like autism. |
| Genetic Component | Genetically modified rats display varied social behaviors related to autism. |
| Future Research | Aim to pinpoint brain circuits responsible for social behavior differences. |
| Data Sharing | Data from research will be made available to the scientific community. |
Summary
Rat behavior and autism are intricately connected through recent research that utilizes innovative AI methods to analyze the social interactions of rats. These discoveries shed light on how variations in behaviors may parallel those observed in individuals with autism. By understanding the genetic and environmental factors influencing these behaviors in rats, researchers hope to unveil crucial insights that could inform future therapeutic strategies for autism in humans.