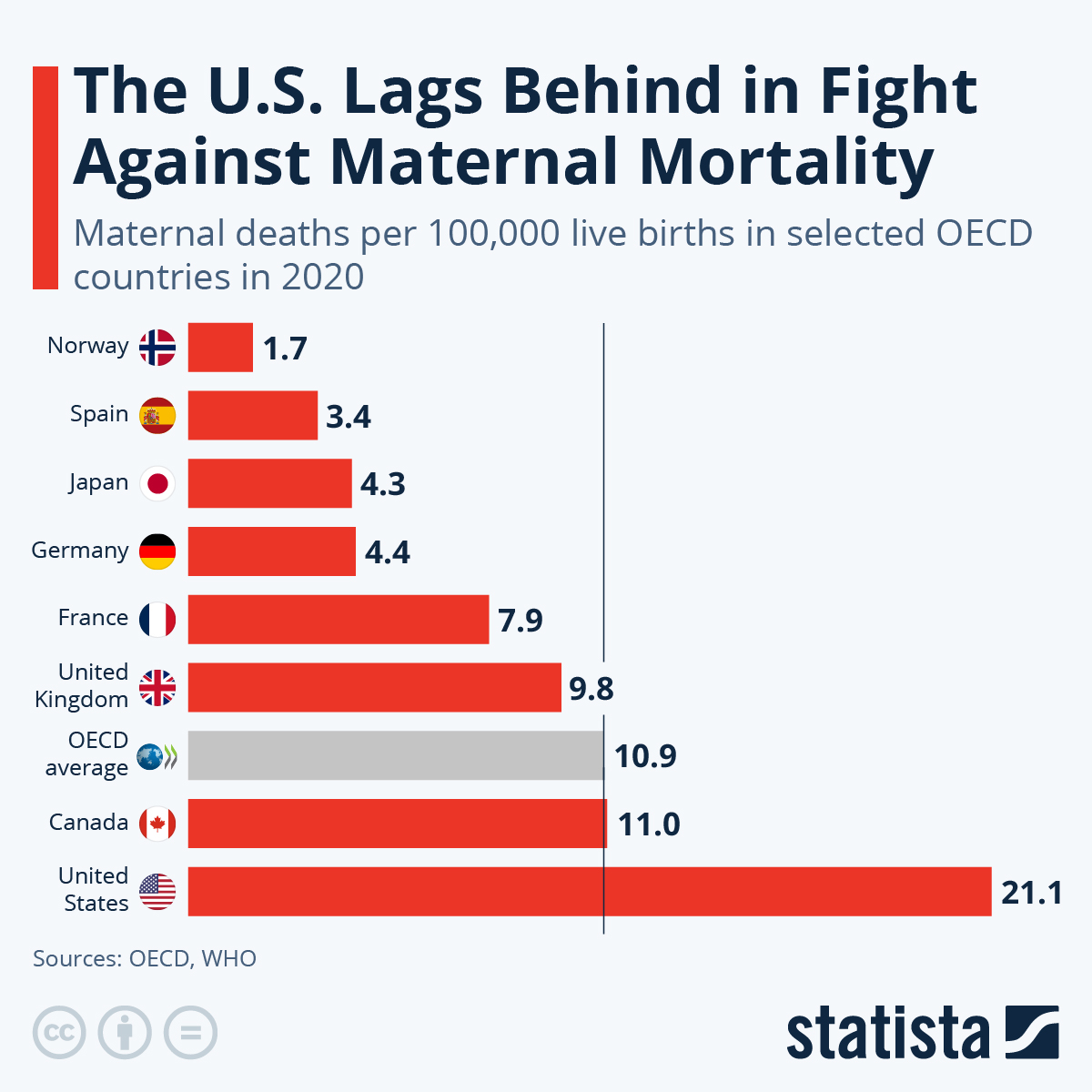
Maternal mortality is a critical issue that continues to challenge the United States, which has the highest pregnancy-related deaths among high-income countries. Alarmingly, over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, highlighting the dire need for improved maternal health initiatives. A recent study underscores this crisis, revealing that maternal mortality rates have risen from 2018 to 2022, disproportionately affecting marginalized groups. The gaps in access to prenatal care and effective postpartum care contribute significantly to these troubling numbers. Addressing these complex issues is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of mothers during and after pregnancy.
The term “maternal mortality” encompasses a range of complex factors surrounding the deaths of women during childbirth or shortly after. Sadly, a significant number of these fatalities can be linked to inadequate pregnancy healthcare and unresolved complications during and after labor. The rising figures of maternal fatalities reveal an urgent need for systemic changes in healthcare systems aimed at enhancing pregnancy-related care. By promoting comprehensive maternal health strategies, particularly in the U.S., we can combat the alarming trend of increased pregnancy complications and ultimately reduce the toll of pregnancy-related deaths. It is imperative that both public awareness and policy reforms focus on strengthening the healthcare framework to protect expectant mothers.
Understanding Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
Maternal mortality rates in the United States have reached alarming levels, particularly during the period from 2018 to 2022. According to recent studies, the U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality, with over 80 percent of these deaths deemed preventable. This reality highlights a critical issue within the nation’s healthcare system, characterized by significant disparities based on race, ethnicity, and geography. Current statistics indicate that American Indian and Alaskan Native women experience mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts, underscoring a dire need for targeted interventions.
Furthermore, cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for more than 20 percent of these tragic outcomes. This shift indicates a troubling trend where chronic conditions, like hypertension, are becoming prevalent among younger women. Thus, addressing maternal mortality requires not only improved healthcare access but also focused initiatives on managing chronic health conditions that can complicate pregnancy.
The Importance of Enhanced Prenatal Care
Prenatal care plays a pivotal role in reducing maternal mortality rates. Comprehensive prenatal services ensure that expectant mothers receive necessary screenings and interventions that can mitigate risks associated with pregnancy complications. Unfortunately, many women in the U.S. lack adequate access to quality prenatal care due to a fragmented healthcare system, with many living in what are termed maternity care deserts. By enhancing access to prenatal care, particularly in underserved communities, we can significantly reduce the rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
Moreover, early and consistent prenatal check-ups allow healthcare providers to identify potential issues early on, such as gestational diabetes or preeclampsia, and manage them effectively. This proactive approach not only improves outcomes for the mother but also enhances the likelihood of a healthy birth for her child. Increasing public health investments in prenatal programs is imperative to address disparities and ensure that all women have access to the care they need.
Postpartum Care: A Critical Component of Maternal Health
While prenatal care has garnered significant attention, the importance of postpartum care cannot be overstated. The U.S. has recognized that maternal health does not end at birth; rather, it extends to the full year following delivery. Currently, late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and a year after childbirth, account for nearly a third of pregnancy-related mortality. This suggests a need for better systems of care that support women in that critical recovery period.
Postpartum care should involve consistent follow-ups, mental health screenings, and management of chronic conditions that may arise or worsen after delivery. By ensuring comprehensive postpartum support, healthcare systems can significantly improve maternal health outcomes and reduce the incidence of late maternal deaths. This holistic approach recognizes the continuum of care necessary for women as they transition into motherhood.
Addressing Racial Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial disparities remain a significant concern in maternal health outcomes across the U.S. Studies highlight that American Indian, Black, and Hispanic women experience substantially higher maternal mortality rates compared to white women. These inequities stem from a complex interplay of systemic biases within healthcare, socioeconomic factors, and access to quality care. To tackle these disparities effectively, targeted policies are essential to address the root causes of inequity in maternal health.
Efforts to create culturally competent healthcare systems, improve diversity within maternal health providers, and establish community-based support programs can help bridge these gaps. Additionally, advocacy for equitable healthcare policies that prioritize vulnerable populations is crucial for meaningful change. By focusing on racial disparities, we can work towards a maternal health system that ensures all women receive the care they require, irrespective of their background.
The Need for Data and Research in Maternal Health
One of the foundational challenges in addressing maternal mortality is the lack of comprehensive data tracking these cases. The introduction of a standardized pregnancy checkbox on death certificates in 2018 marked a significant step towards gathering consistent data on maternal health in the U.S. However, gaps still remain, and ongoing research is needed to fully understand the scope of maternal mortality and the factors contributing to pregnancy-related deaths.
Investing in maternal health research not only provides valuable insights into trends and disparities but also informs evidence-based policy decisions. Continuous monitoring of maternal health outcomes can help identify effective interventions and drive systemic changes necessary for improving care. Therefore, increasing funding and support for maternal health research is crucial for fostering innovations in care and ultimately reducing maternal mortality rates.
Innovative Solutions to Combat Maternal Mortality
To curb the alarming rise in maternal mortality, innovative solutions must be adopted at both policy and practice levels. This includes implementing evidence-based interventions that focus on enhancing the quality of care during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Programs that incorporate telehealth services, community health workers, and mobile health applications can bridge the gap for women who lack access to traditional healthcare systems, particularly in rural or underserved areas.
Additionally, education programs that empower women to understand their health and wellness before, during, and after pregnancy can lead to better outcomes. Fostering collaboration among healthcare providers, community organizations, and policymakers can create a comprehensive support network that addresses barriers and promotes maternal health. Such innovative strategies are vital to reducing preventable pregnancy-related deaths and improving overall maternal health in the U.S.
Impact of Healthcare Infrastructure on Maternal Health
The healthcare infrastructure in the U.S. is often cited as a primary factor influencing maternal health outcomes. The fragmented system, characterized by unequal access and varying quality of services, has contributed to the rising rates of maternal mortality. Strengthening the healthcare infrastructure involves not only increasing funding for maternal health services but also ensuring that care is equitable and accessible across all demographic groups.
Integrating maternal health services within existing healthcare frameworks and enhancing public health initiatives can greatly improve care delivery. This includes ensuring that prenatal and postpartum services are not only available but also adequately funded. By investing in healthcare infrastructure, we can create a more supportive environment for expectant and new mothers, ultimately reducing pregnancy-related deaths.
The Role of Policies in Maternal Health Improvement
Policy plays a critical role in shaping maternal health outcomes. Legislative efforts that prioritize maternal health access, funding for prenatal and postpartum care, and the elimination of healthcare disparities can significantly impact mortality rates. For instance, states that have implemented more comprehensive maternal health policies, such as extended Medicaid coverage during the postpartum period, have seen improvements in maternal health outcomes.
Advocating for comprehensive policies at local, state, and national levels is essential to reforming the maternal healthcare landscape. Policymakers must prioritize maternal health by considering the intersection of various factors including economic stability, healthcare access, and community services. Meaningful policy changes can lead to reduced disparities and improved health outcomes for all mothers.
Raising Awareness for Maternal Health Challenges
Raising awareness about maternal health challenges is crucial for fostering community engagement and driving action. Many individuals, particularly in marginalized communities, are unaware of the risks associated with pregnancy-related complications or the resources available to them. Campaigns that educate and inform the public about maternal health issues can empower women and families to seek care and advocate for themselves.
Community engagement initiatives that involve local leaders and healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in increasing awareness. These programs can provide vital information on the importance of prenatal and postpartum care, mental health resources, and chronic disease management. By mobilizing communities to address maternal health challenges collectively, we can work towards reducing disparities and improving care quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is maternal mortality and how does it relate to pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal mortality refers to deaths due to complications from pregnancy or childbirth. It is a key indicator of maternal health, particularly in the USA, where pregnancy-related deaths continue to rise. Understanding this term is critical as it highlights the preventable nature of a majority of these deaths.
What are the main causes of maternal mortality in the United States?
The leading causes of maternal mortality in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, complications from obesity, and insufficient access to prenatal care. Addressing these factors is essential for improving maternal health and reducing pregnancy-related deaths.
Why does the U.S. have a higher maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has a higher maternal mortality rate due to various systemic issues, including inequitable healthcare access, systemic bias, and chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals, which are exacerbating pregnancy complications.
How does prenatal care influence maternal mortality rates?
Quality prenatal care is crucial for monitoring and addressing health complications during pregnancy, thus significantly lowering maternal mortality rates. Early and regular prenatal check-ups can help identify risks and improve outcomes for both mothers and babies.
What are the implications of late maternal deaths on overall maternal health statistics?
Late maternal deaths, occurring up to one year postpartum, significantly impact maternal health statistics and demonstrate the need for ongoing care beyond the initial postpartum period. Addressing postpartum health is vital for reducing overall maternal mortality rates.
What role do racial disparities play in maternal mortality in the USA?
Racial disparities in maternal mortality rates reflect systemic inequities in healthcare access and quality among different racial and ethnic groups. For example, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest rates of pregnancy-related deaths, indicating a need for targeted health interventions.
How can postpartum care impact maternal health outcomes?
Effective postpartum care is essential in preventing complications that may lead to maternal mortality. It ensures that women receive the necessary support and treatment during the recovery phase, thereby reducing risks associated with childbirth.
What recent trends have been observed in maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Recent trends show a continued rise in maternal mortality rates in the U.S., particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Data from 2022 indicated a sharp increase compared to previous years, emphasizing the need for improved maternal health initiatives.
What strategies can be implemented to reduce maternal mortality rates in the USA?
To reduce maternal mortality, strategies may include enhancing prenatal and postpartum care, improving healthcare access, addressing chronic health issues in reproductive-age individuals, and implementing state-level policies to standardize quality care across the country.
How can individuals advocate for better maternal health policies?
Individuals can advocate for better maternal health policies by participating in public health discussions, supporting community health programs, contacting policymakers, and raising awareness about the importance of comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, continuing to rise. In 2022, the rate was 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, indicating significant gaps in care. |
| Racial Disparities | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women having the highest mortality rate (106.3 per 100,000 live births) compared to white women (27.6) and non-Hispanic Black women (76.9). |
| Impact of COVID-19 | An increase in maternal mortality rates was noted during the COVID pandemic, particularly in 2021. |
| Need for Better Care | Improving prenatal and postpartum care, particularly addressing the needs of various racial groups and chronic health conditions, is essential. |
Summary
Maternal mortality remains a critical health issue in the United States, with rates continuing to rise despite the high percentage of preventable deaths. The stark racial disparities and the impact of chronic conditions highlight the urgent need for systemic changes in healthcare policies and practices. Investments in comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care are essential to reverse these trends and ensure safer pregnancies for all women.