The groundbreaking discovery of microRNA transformed our understanding of gene regulation, a revelation first brought to light by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his collaborator, Victor Ambros, in 1992. Initially, their research on the C. elegans roundworm barely captured the attention of the scientific community; however, it soon became clear that microRNAs play a pivotal role in the regulation of genes across various species, including humans. This exploration into the world of tiny RNA molecules, supported largely by NIH funding, would later pave the way for significant advancements in medical therapies targeting diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s. As the field expanded, microRNA emerged not simply as a curiosity, but as a foundational component essential for understanding biological processes. Ruvkun’s work not only earned him a Nobel Prize but also ignited a global interest in microRNA research, solidifying its place in the pantheon of molecular biology.
The advent of small non-coding RNA molecules, known as microRNAs, marked a significant evolution in the landscape of genetic research and regulation. Pioneered by the early investigations of scientists like Gary Ruvkun, this field uncovered crucial insights into how genetic expression is modulated in organisms such as the C. elegans roundworm. Despite initial skepticism, later findings revealed that these microRNAs are integral to not only simple life forms but also complex human biological systems. The quest for understanding these molecules, primarily fueled by government-backed initiatives and NIH funding, has opened new avenues in medical science, particularly in developing therapies aimed at a range of diseases. As interest continues to grow globally, the influence of microRNA in regulating the genetic machinery remains a focal point of contemporary biological research.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of microRNA
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros made a pivotal discovery that would change the landscape of genetic research: the identification of microRNA. Initially met with skepticism, their findings published in the journal Cell revealed a novel layer of gene regulation in the C. elegans roundworm. This small, yet revolutionary, RNA molecule plays a crucial role in controlling gene expression across various species, including humans. The impact of this breakthrough has only been acknowledged years after its inception, proving the initial hesitance of the scientific community to fully grasp the significance of their work.
The journey from their first publication to being awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 2024 reflects the gradual shift in perception of microRNA’s importance in gene regulation. The nuances of how these small RNA molecules function led to a broader understanding, paving the way for significant advancements in biomedicine. As therapies based on microRNA are now under investigation for various diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s, the once-overlooked discovery is now recognized as a cornerstone of genetic research, illustrating how revolutionary ideas can take time to be fully appreciated.
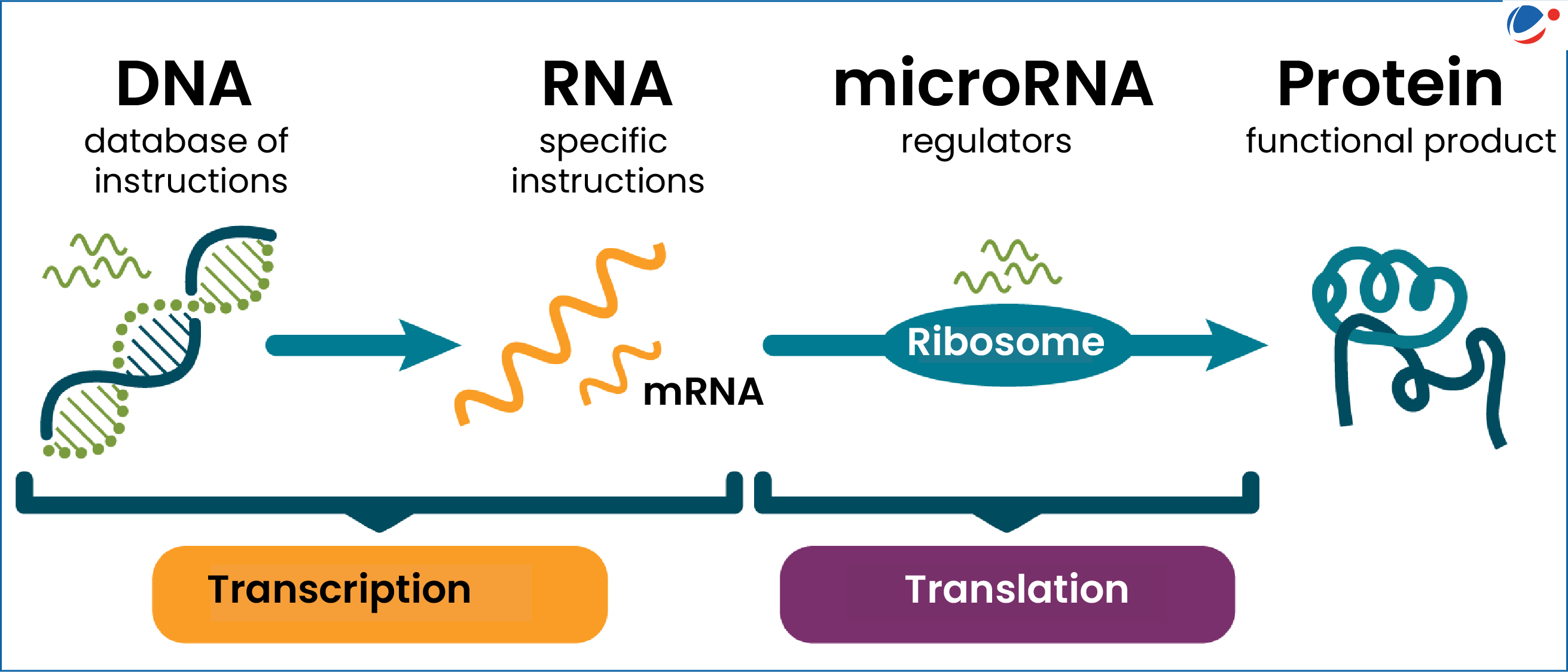
Fundamental Role of microRNAs in Gene Regulation
MicroRNAs are now understood to be essential components in the regulation of gene expression, influencing how organisms develop and function. The discovery that the human genome contains approximately 1,000 microRNAs underscores their significance in managing the production of proteins vital for cellular operations. This regulatory capacity links directly to various physiological processes, demonstrating that microRNAs are indispensable for understanding health and disease mechanisms.
The involvement of microRNAs in gene regulation has sparked numerous studies, revealing their critical role in a variety of diseases. Researchers are actively exploring how these tiny molecules can be harnessed for therapeutic purposes. For instance, clinical trials are ongoing to assess their efficacy in treating heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. The recognition of microRNAs as vital regulators not only enhances our understanding of biology but also offers promising avenues for innovative treatment strategies.
Funding Success and Challenges in Scientific Research
Gary Ruvkun’s research journey has been significantly supported by federal funding, primarily from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). For over four decades, approximately 75% of his lab’s funding has come from the government, allowing his team to explore innovative avenues in genetics. This financial support has been crucial in sustaining a small but efficient lab, where dedicated researchers conduct high-level scientific inquiry without the overwhelming financial pressures faced by some larger institutions.
However, Ruvkun expresses concern regarding the future of federal funding for science research. Given the significant role that government investment has played in advancing technological and medical breakthroughs, he fears that cuts could hinder the next generation of scientists. By investing in research, especially in fields like gene regulation and microRNA discovery, the government has historically contributed to the United States’ status as a leader in scientific innovation, and Ruvkun advocates for continued support to ensure ongoing advancements.
The Evolution of Scientific Recognition
In the early years following the discovery of microRNA, Ruvkun and Ambros faced a lack of immediate recognition within the scientific community. The initial disinterest in their findings indicated a broader challenge faced by groundbreaking researchers: the slow evolution of scientific recognition. Despite the eventual validation of their work through a prestigious Nobel Prize, it took years for the full impact of their discovery to be acknowledged by their peers and the global research community.
Such delayed recognition is not uncommon in scientific research, as paradigm-shifting discoveries often require time to be understood and accepted. Ruvkun’s experience illustrates the importance of perseverance in the face of skepticism, highlighting how groundbreaking ideas can shape future research directions and lead to significant advancements in understanding complex biological mechanisms.
Implications of microRNA Research in Medicine
The implications of microRNA research extend far beyond basic biology into the realm of clinical medicine. With ongoing clinical trials exploring the applicability of microRNAs in treating a wide range of diseases, researchers are beginning to translate these fundamental discoveries into tangible health solutions. For example, microRNA therapies are being investigated for their potential to combat chronic conditions such as heart disease and various cancers, promising a new frontier in medicine that is both innovative and hopeful.
The momentum generated by microRNA research underscores the vital link between basic research and clinical applications. As scientists continue to elucidate the mechanisms by which microRNAs regulate gene expression, the pursuit of targeted therapies could lead to breakthroughs in the management of complex diseases. This nexus of research exemplifies how foundational discoveries can impact patient care and therapeutic development, reinforcing the importance of ongoing investment in scientific discovery.
Research Collaborations and Community Impact
The growth of interest in microRNA and gene regulation has fostered a vibrant community of researchers who collaborate across various disciplines. As the RNA field continues to expand, scientists from different backgrounds are engaging in interdisciplinary efforts to explore the relevance of microRNAs. This collaborative spirit not only accelerates the pace of discovery but also enriches the dialogue among scholars, leading to a more holistic understanding of gene regulation.
Ruvkun’s acknowledgment of the ‘worm community,’ which initially drove interest in their findings, highlights the importance of localized research communities in nurturing scientific progress. The synergy generated by these collaborations has propelled microRNA research into the foreground of genetic studies, illustrating how collective efforts among scientists can lead to transformative advancements in our understanding of biology and medicine.
The Future of microRNA Therapeutics
Looking ahead, the future of microRNA therapeutics appears promising, with various studies underway to unlock the potential of these small RNA molecules. Following the successful identification of microRNAs and their roles in gene regulation, researchers are now focusing on developing therapies that harness their capabilities. This pursuit not only involves investigating their therapeutic effects but also understanding the safety and efficacy of microRNA-based treatments in clinical settings.
As interest in microRNA research continues to grow, so too does the potential for novel pharmaceutical applications. With significant investments in research and development, the landscape is evolving to incorporate microRNA-based solutions for previously challenging medical conditions. As new discoveries emerge from ongoing clinical trials and laboratory studies, the integration of microRNA therapeutics into mainstream medicine could radically change how diseases are treated and managed.
The Role of NIH Funding in Scientific Progress
Federal funding, particularly from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has long been a crucial element for scientific inquiry in the United States. For researchers like Gary Ruvkun, the support from NIH has been instrumental in advancing their work and fostering innovations in gene regulation and microRNA discovery. This funding not only empowers scientists to explore their hypotheses but also catalyzes broader scientific discussions that contribute to our understanding of complex biological phenomena.
Despite the invaluable contributions of NIH funding to groundbreaking discoveries, the threat of reduced federal investment looms over the scientific community. Concerns about future funding cuts can deter young scientists from pursuing research careers, creating a potential gap in innovation. Ruvkun’s advocacy for sustained funding highlights the importance of government support in maintaining the United States’ leadership role in scientific research and discovery.
Translating Basic Research into Commercial Success
The intersection of basic research and commercial application is exemplified by companies that have emerged from foundational discoveries, such as microRNA research. The success of firms like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, which focuses on RNA interference therapeutics, showcases how academic discoveries can lead to significant advancements in the biotech industry. With a focus on transforming scientific insights into viable products, the collaboration between researchers and industry has the potential to revolutionize treatment options for various genetic diseases.
This translation from discovery to commercial success highlights the broader implications of research funding and support. By investing in scientific research, regulatory bodies not only contribute to our understanding of biology but also foster an environment where new technologies can flourish. As researchers like Ruvkun continue to make strides in the field of microRNA, the evolution of innovations into commercially viable solutions signifies the profound impact of fundamental research on human health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA discovery and why is it significant in gene regulation?
MicroRNA discovery refers to the identification and characterization of small RNA molecules that play crucial roles in gene regulation. These tiny RNAs, first discovered in the 1990s by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros, are essential in controlling gene expression and protein synthesis in various organisms, including humans. Their significance lies in their ability to regulate approximately 1,000 human protein-producing genes, making them pivotal in understanding cellular processes and developing therapeutics for diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the field of microRNA discovery?
Gary Ruvkun significantly contributed to microRNA discovery through his research on the C. elegans roundworm, where he revealed that these small RNA molecules could regulate gene expression. His findings, published in 1993, initially received limited attention but laid the groundwork for understanding the broader implications of microRNAs in genetic regulation across species, earning him the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
What role do NIH grants play in supporting microRNA discovery research?
NIH grants have been instrumental in supporting microRNA discovery research. Gary Ruvkun, whose work was primarily funded by the National Institutes of Health, emphasizes that such funding has enabled breakthrough research that has become foundational in the field. The federal support over decades has allowed scientists to explore microRNA functions, leading to advancements in understanding gene regulation and the development of RNA-based therapies.
How are microRNAs involved in clinical therapies for diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer?
MicroRNAs are involved in clinical therapies for diseases such as Alzheimer’s and cancer because they can directly influence gene expression related to disease pathogenesis. Research into microRNA functions has led to innovative therapeutic approaches that aim to restore or modify the activity of specific microRNAs, which are currently being tested in clinical trials for their effectiveness in treating these conditions.
What impact has microRNA discovery had on the biotechnology industry?
MicroRNA discovery has significantly impacted the biotechnology industry by spurring the development of companies focused on RNA therapeutics, such as Alnylam Pharmaceuticals. These companies, driven by research into microRNAs and RNA interference technologies, have become key players in the biotechnology sector, innovating treatments for genetic diseases and establishing a thriving industry that builds upon foundational research supported by federal funding.
Why is microRNA research considered essential for understanding human biology?
MicroRNA research is considered essential for understanding human biology because these molecules are fundamental to the regulation of gene expression and the translation of genetic information into functional proteins. As key regulators of multiple biological processes, microRNAs help elucidate the complexities of development, maturation, and the cellular response to environmental signals, making them critical for advancing our knowledge in genetics and disease biology.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in C. elegans, revealing a new level of gene regulation. |
| Initial Reception | Their findings initially received little attention from the evolutionary biology community. |
| Funding and Support | Most of their research has been supported by NIH grants, allowing them to continue their work. |
| Impact on Diseases | MicroRNA therapies are now being tested for various diseases, including heart disease and cancer. |
| Evolution of Interest | Interest in microRNA grew exponentially within the RNA research field, leading to significant scientific advancements. |
| Ruvkun’s Perspective | Ruvkun emphasizes the importance of federal funding in driving scientific success and innovation. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery has significantly shaped our understanding of gene regulation and has opened up new avenues for medical therapies. The groundbreaking work of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in uncovering the role of microRNAs over three decades ago has led to advancements in treating major diseases. Today, ongoing research and clinical trials highlight the essential functions of microRNAs in human health, further underscoring their importance in molecular biology.